Photovoltaic power generation has graduated from the feed-in tariff system (FIT system) and has entered the stage of exploring popular models such as self-consumption and solar sharing (farming solar). Among them, it will be necessary to utilize subsidies for the introduction of power generation equipment, which is still expensive.
Therefore, this time, we have summarized the main subsidy programs related to solar power from the new fiscal year.
Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry supports “consumer-driven”
The main subsidies from the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry are consumer-led solar subsidies. The official name is "Consumer-driven photovoltaic power generation and renewable energy power supply combined storage battery introduction support project cost subsidy". This can be used when electricity consumers install photovoltaic power generation facilities that do not rely on FIT, FIP (feed-in premium) systems, or self-consignment, and use renewable energy over the long term. In short, it is mainly a self-consumption type solar installation subsidy, with a budget of 16.5 billion yen.
The main requirements are that "the power generation company will install a new photovoltaic power generation facility with a total capacity of 2 MW or more", "use contract for a certain amount or more for 8 years or more", and "multiple companies and multiple facilities are acceptable as consumers".
The subsidy rate is less than 1/2 for the regular type, less than 2/3 for the municipal cooperation type, and less than 1/3 for the attached storage battery (Fig. 1).
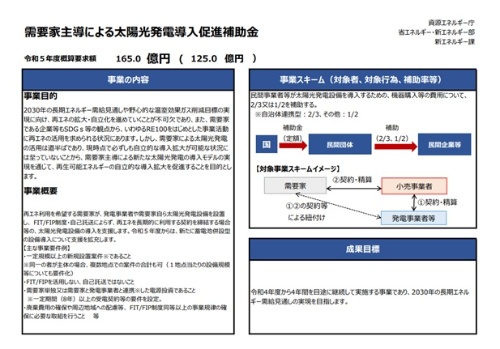
Fig. 1 Outline of subsidy system to support installation of new solar power plants led by consumers
(Source: Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry, budget explanatory material,
https://www.meti.go.jp/main/yosangaisan/fy2023/pr/en/shoshin_taka_33.pdf)






