Fujita et al./Efficient removal of sediment from dam lakes, prevent water pollution, and support high water depths
System overview (from press release materials)
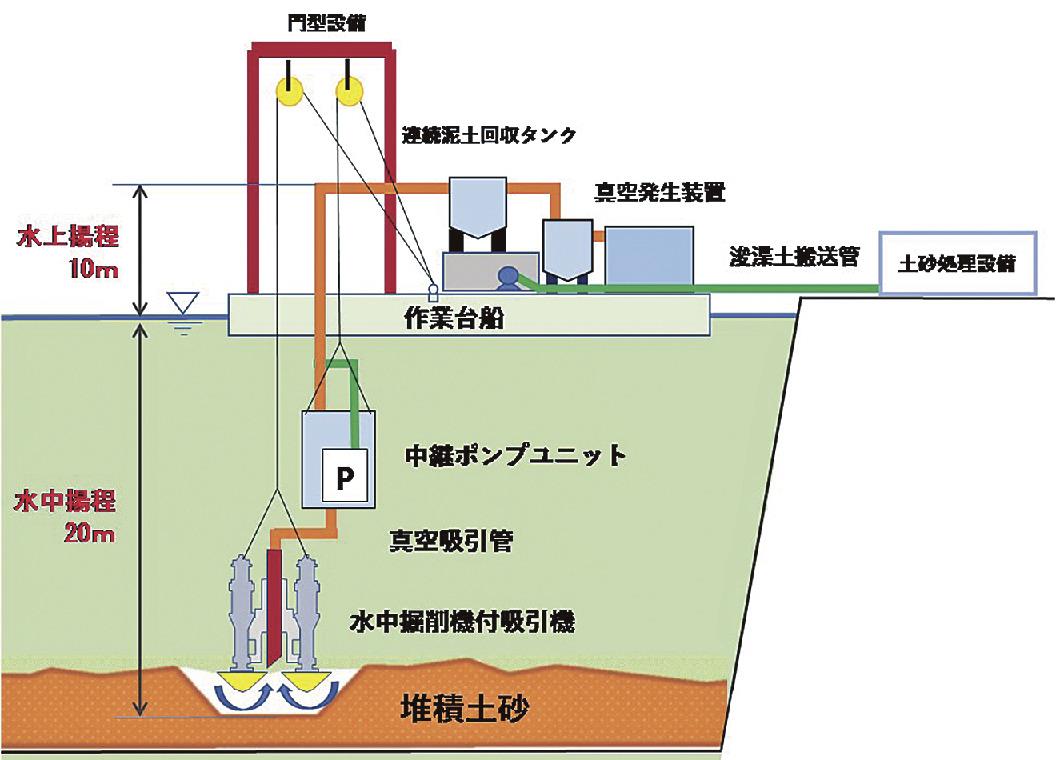
Fujita and Kawamoto Gumi (CEO, Akiota Town, Hiroshima Prefecture, Kazuo Kawamoto) have developed a dredging method that can prevent water pollution of the dam lake and remove the sediment on the bottom of the dam at a suction height (lift) of 20 meters or more. The prefabricated pontoon is equipped with a high-performance vacuum generator and a relay pump unit "high-concentration agitation pump" that conveys mud. Sediment can be efficiently removed even at a lift of 10 meters or more above the water, which was not possible with vacuum suction alone.
Currently, there are more than 100 dams nationwide whose functions have deteriorated due to the sedimentation of dam lakes. Water pollution was unavoidable with conventional methods such as using a small dredging pump ship or draining water and removing it with heavy machinery. There is also a vacuum suction method that does not pollute the water quality, but there is a problem that it cannot be used in dams with deep water.
The developed "high lift non-turbid dredging method" can suppress the generation of pollution and remove sediment even at a lift of 20 meters or more. Dredging work can be performed while generating electricity even near the intake facility of an electric power dam, which was difficult due to the occurrence of pollution.
The main equipment consists of a suction machine with an underwater excavator, a relay pump unit, a large continuous mud recovery tank, and a vacuum generator. Two high-torque underwater excavators excavate the sediment deposited on the bottom of the lake and gravel with a particle size of 40 mm or less, and suck it before the sediment diffuses. By using a high-concentration stirring pump together, it exhibits high transport capacity even when there is a lift of 20 meters or more.
The pontoon uses a combination of multiple Unifloats (about 2 meters x about 4 meters, weight 4 tons). It has excellent transportability and can meet various construction conditions by changing the number. The ICT construction management system that utilizes GNSS (Global Positioning Satellite System) can grasp the construction status in real time, and the number of workers, which used to be about five, can be reduced to one.
Test construction was conducted at four dams in Hiroshima prefecture, including electric power dams, and it was confirmed that sediment could be removed from a depth of 20 meters and a height of 10 meters above the water. In the future, we will improve the efficiency of dredging work on dam lakes, which have various restrictions, and develop it as a technology to support the extension of the life of dams.






